Therapies
The ultimate goal of cancer therapy is to eliminate both the tumour and circulating cancerous cells without harming healthy tissue. Despite the numerous therapies available today, total remission cannot be achieved for all cancers. The complexity of the disease makes developing safe and efficient treatments particularly difficult. The search queries in this section illustrate the range of tools available to oncologists and the multimodal approaches that can be used to attack cancer cells, reduce their spread and induce a systemic anti-cancer immune response against the primary tumour and metastases.
- Surgery
-
The following datasets relate to invasive interventions that aim to ablate the solid tumour or at least shrink it. They cover patent documents aiming at improving the resection of the tumour without harming the surrounding tissues and the patient.
Conventional surgery
High-precision surgery includes any type of computer-aided surgery (CAS) with image-based planning and manual or (semi-)automatic execution. It includes real-time matching of pre-surgical images with live images to guide the surgeon to the regions of interest. Markers may be used to support the planning or ease repeated access.
Computer-aided surgery and robotics
Treatment by cooling
Cooling therapy can be used during surgery to protect healthy tissue and reduce the risk of side effects. Cooling therapy may also be used to destroy cancer cells by freezing the tumour and surrounding tissue to provide a safety margin. The frozen tissue may then be removed surgically.
In combination with an ultrasonic implement
In combination with conventional excision surgery
Treatment by heating
Cancer surgery heating, also known as thermal ablation, is a treatment that uses heat to destroy tumour cells. It can be performed during surgery or as a minimally invasive procedure. The use of heat can also reduce bleeding associated with surgery.
Coagulation with conventional excision surgery
Passing current through tissue
Localised ultrasound hyperthermia
Coagulation treatment with single instrument
Cell poration
This cancer treatment can be performed during surgery and uses electrical pulses to create pores in the cell membrane. This allows therapeutic agents to enter the cell more easily and kill the cancer cells.
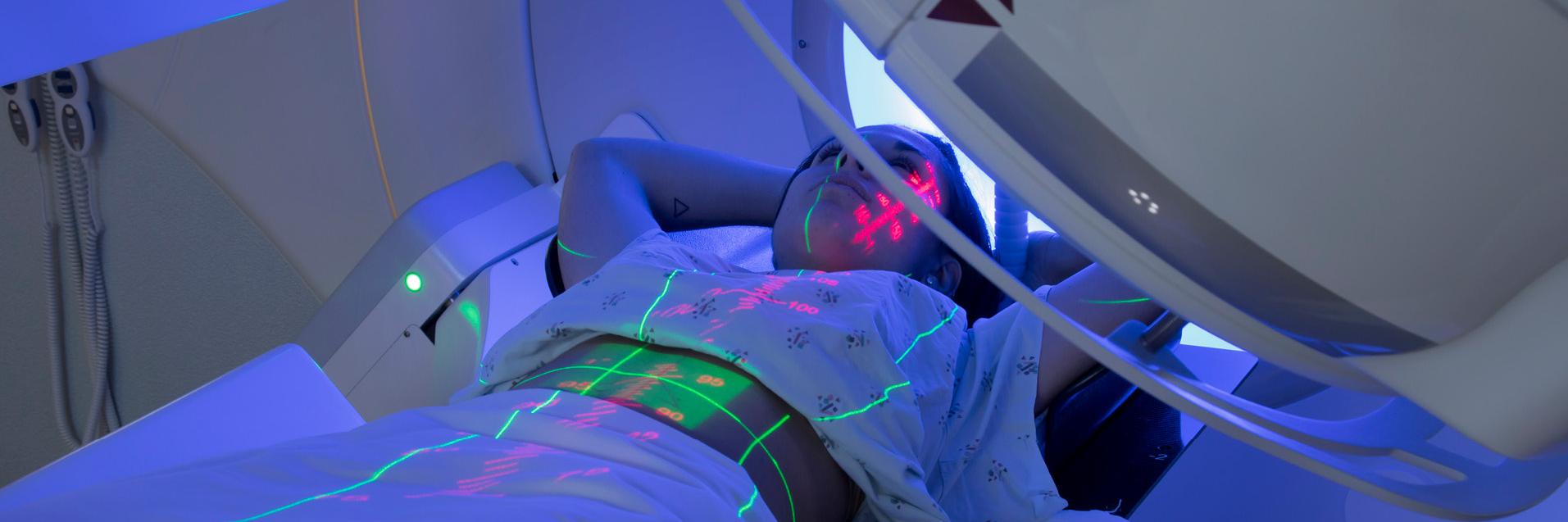
- Radiotherapy
-
Radiotherapy, or radiation therapy, uses ionising radiation to kill cancer cells by damaging their DNA. The process of cancer cell death and their removal by the body takes place sometime after exposure to ionising radiation, i.e. the death of cancer cells is not immediate. There are two main radiotherapy types depending on how the radiation is delivered: radiation sources are brought near to the cancer cells (brachytherapy) or radiation is targeted at the cancer cells from outside the body (external radiotherapy).
Brachytherapy
In brachytherapy, radiation sources are placed inside or next to the tumour. This allows a higher dose of radiation to be delivered to the cancer cells while minimising damage to healthy tissue.
General aspects of brachytherapy
The following datasets distinguish different brachytherapy types based on the delivery location of the radiation source:
Delivered to body lumens, e.g. vessels
Intraluminal radiation therapy
Delivered to natural body cavities or cavities generated by surgery
Intracavitary radiation therapy
Delivered through the patient's skin, e.g. using needle-like devices
Interstitial radiation therapy
External radiotherapy
In external radiotherapy, high-energy X-rays or particle beams are directed at the tumour from outside the body. The accuracy of the beam's location and the control of its intensity are essential to provide an effective treatment that reduces damage to the surrounding healthy tissues. The following datasets concern specific aspects of external radiotherapy:
Radiation is guided in real time using medical images
Adaptation of treatment parameters to changes in a patient's anatomy or to previous treatments
Modulation of the beam intensity using e.g. multi-leaf collimators
Intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT)
Modulation of the beam intensity during movement of a gantry
Intensity-modulated arc therapy (IMAT)
Use of proton or ion beams
Radiotherapy using charged particles
Particles are generated by target irradiation with laser light
Particle beam generation using lasers
Ultra-high-dose-rate radiotherapy, i.e. higher than 40 grays per second
Use of an isotope such as boron-10 to emit highly localised alpha particles (NCT)
Radiotherapy planning with AI
The following dataset relates to the use of artificial intelligence (AI) in radiotherapy planning to improve the accuracy, efficiency and consistency of radiotherapy planning, leading to better patient outcomes. AI algorithms can automate and enhance various aspects of the planning process, leading to a significant reduction in the time needed for planning.
- Photodynamic therapy
-
Photodynamic therapy is a minimally invasive treatment that uses light and a photosensitiser to kill cancer cells. The photosensitiser is delivered to the cancer cells, e.g. by injection into the bloodstream or application to the skin. After its exposure to light of a specific wavelength, it produces reactive oxygen species that kill cancer cells.
- Hyperthermia
-
Hyperthermia is an adjuvant to cancer treatment and involves heating body tissues to temperatures above physiologically normal values in the range of 40-43°C that are not high enough to directly destroy the cells. Hyperthermia apparatus use energy sources such as radio waves or microwaves to heat cancer cells. Hyperthermia is normally used in combination with (as an adjuvant to) radiotherapy and/or chemotherapy.
- Classical chemotherapy
-
Because they have acquired genetic mutations, cancer cells are highly proliferative. A further consequence of the genetic mutations is a lack of control and repair of genome damage. Chemotherapy targets the fast-growing cells and induces their death by necrosis, apoptosis or autophagy, e.g. through induction and accumulation of DNA damage or through inhibition of cell division. The following datasets relate to classes of chemotherapeutic agents.
Alkylating and alkylating-like agents
Non-alkylating agents
Non-alkylating DNA-damaging agents and topoisomerase inhibitors
Anti-metabolites
Anti-pyrimidines and cytidine analogues
Anti-microtubule agents
- Targeted therapy
-
Research over the past decades has unravelled the signalling pathways activated by cancer cell mutations that promote cancer cell proliferation, change in differentiation (epithelial-mesenchymal transition), angiogenesis and dissemination. Treatments based on this research target a cancer's specific genes, proteins or tissue environment (including blood vessels) that contribute to its growth and survival. These treatments are more focused and often cause fewer side effects than chemotherapy. These datasets therefore cover patent documents relating to the targeting of specific pathways activated in cancer cells, which ultimately leads to tumour growth reduction or even tumour eradication.
Protein kinase inhibitors
Receptor protein kinase inhibitors
Receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) are essential in regulating cellular processes such as growth, differentiation, metabolism and motility. RTKs transduce extracellular signals to the cytoplasm. Receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors (R-TKIs) reduce phosphorylation and hence activation of their substrates and inhibit the proliferation or survival of cancer cells.
Non-receptor protein kinase inhibitors
Non-receptor tyrosine kinases (NRTKs) are intracellular proteins that relay signals essential in regulating cell adhesion or cell growth. Non-receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors (NR-TKIs) reduce phosphorylation and hence activation of their substrates and accordingly block activation of downstream signalling pathways that favour the survival or proliferation of cancer cells.
Serine/threonine kinase inhibitors
Serine/threonine kinases are essential in regulating cell growth and cell division.
Hedgehog pathway inhibitors
Hedgehog (Hh) pathway inhibitors, such as sonidegib, vismodegib, glasdegib or arsenic trioxide, are drugs that inhibit hyperactivated Hh signalling, which is involved in the carcinogenesis and/or self-renewal of cancer stem cells in cancers of the skin, brain, liver, prostate and breast and in haematological malignancies.
MDM2 inhibitors
MDM2 inhibitors provide anti-tumour effects in cancers with a wild-type or functional TP53 gene, which encodes the tumour suppressor p53. The tumour suppressor is activated by cellular stress or DNA damage. This may lead to cell cycle arrest, DNA repair and apoptosis, but in tumour cells, p53 is often downregulated, e.g. by overexpression of the MDM2 gene and accumulation of the MDM2 protein, which promotes the degradation of p53. MDM2 inhibitors such as idasanutlin, navtemadlin and siremadlin re-activate p53, exerting its strong anti-tumour activity.
Proteasome inhibitors
Proteasome inhibitors (PIs) induce the accumulation of unfolded and misfolded proteins in cells, leading to growth arrest, apoptosis and cell death. Cancer cells may have a higher content of abnormal proteins than normal cells and are more sensitive to PIs (e.g. bortezomib, ixazomib or carfilzomib).
PARP inhibitors
PARP inhibitors are drugs that inhibit poly(ADP-ribose) polymerases (PARPs), enzymes involved in the repair of DNA single-strand breaks. They prevent the repair of DNA damage in cancer cells. The genomic instability of tumour cells explains, at least partially, the selectivity of PARP inhibitors for tumour cells over normal cells.
Inhibitors of apoptosis-related proteins
The anti-apoptotic members of the BCL-2 family, BCL-2, BCL-XL, MCL-1 and BCL-w, are pro-survival proteins and established or potential targets of anti-cancer therapy in specific haematological malignancies. Inhibition of these pro-survival proteins has been demonstrated to provide effective anti-cancer effects, e.g. venetoclax in CLL, acute myeloid leukaemia or DLBCL.
Inhibitors of apoptosis-related proteins of the BCL-2 family
GTPAse K-RAS inhibitors
K-Ras is an oncogene activated in tumour cells that induces uncontrolled cell proliferation.
Epigenetic inhibitors
Gene expression can be modulated in cancer cells by epigenetic modulation, i.e. modification of the accessibility of the genomic DNA, e.g. by methylation or acetylation. This modification can result in the activation of genes controlling cell proliferation. Epigenetic inhibitors aim to shut down this activation. For example, epigenetic inhibitors of the histone methyltransferase "enhancer of zeste homolog 2" (EZH2) lead to tumour regression via inhibition of the trimethylation of H3K27.
Angiogenesis inhibitors
Cancer cells induce the formation of new blood vessels (angiogenesis) that provide nutrients to support their growth and result in the spread of tumour cells that infiltrate the blood vessels. Angiogenesis inhibitors inhibit the formation of new blood vessels and are particularly effective against solid tumours, i.e. by starving them of blood.
- Hormonal therapy
-
Hormones are proteins or small molecules known as chemical messengers that co-ordinate and control the function of organs in the body. Some hormones act as growth factors and increase cancer growth, such as in breast or prostate cancer. The following searches relate to various classes of compounds that antagonise or regulate hormones produced by the body.
- Immunotherapy
-
Cancer cells can be distinguished from healthy tissue by the presence of mutated proteins or exogenous proteins, e.g. viral oncogenes. The immune system can therefore detect and destroy cancer cells based on these antigens or neoantigens. Cancer cells can escape the immune system by expressing proteins that block the immune response. Immunotherapy aims at boosting the immune system to fight cancer.
Vaccines
Vaccines induce the production of antibodies and cytotoxic immune cells that specifically target the cancer cells. The vaccines are based on antigens specifically expressed by the tumour cells being targeted. The following datasets include patent documents generally relating to cancer vaccines and are limited to the nature of the immunogen or the delivery method.
Antibodies and immunomodulation
Antibodies can be administered to the patient to target specific molecules expressed at the surface of cancer cells or to activate anti-cancer immune cells. This dataset relates to a class of antibodies that block proteins stopping the immune system from attacking the cancer cells. They therefore enhance anti-cancer immunotherapy.
Cellular immunotherapy, including CAR-T cell therapy
This dataset relates to modifying the patient's immune cells, often T lymphocytes, to target specific markers expressed at the surface of the cancer cells and induce cytolysis of the cancer cells. This includes the CAR-T cell technology that is particularly effective against liquid cancers (leukaemia, lymphoma, myeloma).
Immunomodulators
The following searches relate to classes of compounds that stimulate the anti-cancer immune response and support the targeting of the cancer cells by the patient's own immune system:
Adenosine receptor antagonists
Oncolytic viruses
Oncolytic viruses are those which infect, replicate and specifically kill tumour cells, either naturally or after genetic engineering. The combination of the viral infection and the release of cancer antigens by the killed tumour cells stimulates a systemic anti-cancer immune response. This response can be amplified by arming the oncolytic virus with immunomodulators.